The History of Cybersecurity Awareness Month
National Cybersecurity Awareness Month was launched in 2004 by the Department of Homeland Security to bring cybersecurity awareness to Americans. Since then, it has evolved into a collaborative event that includes other government entities such as the FBI and cybersecurity experts worldwide.

Today, National Cybersecurity Awareness Month is an industry-wide effort held each October to increase awareness of cyber threats. The goal is to help organizations safeguard their people, data, and systems. Cybersecurity vendors offer their latest findings, provide tips and publish educational material to help businesses educate their workforce.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Awareness
Cybersecurity threats are constantly changing. What saved you from an attack last year may not be enough to protect you this year. This is when cybersecurity awareness training for employees becomes invaluable: it’s not just about theory, but about the day-to-day actions employees should take when needed.
For example:
- Recognizing a phishing email.
- Enabling multifactor authentication.
- Selecting strong, distinct passwords.
- Reporting suspicious behaviour at the earliest signs.
Employees that undergo training on a regular basis become the first line of defense. They can potentially identify and stop threats before they do damage.
With small and medium-sized organizations, where resources may often be stretched thin, it can be the difference between remaining secure and becoming a victim of an attack.
What does modern malware do that your systems don’t see?
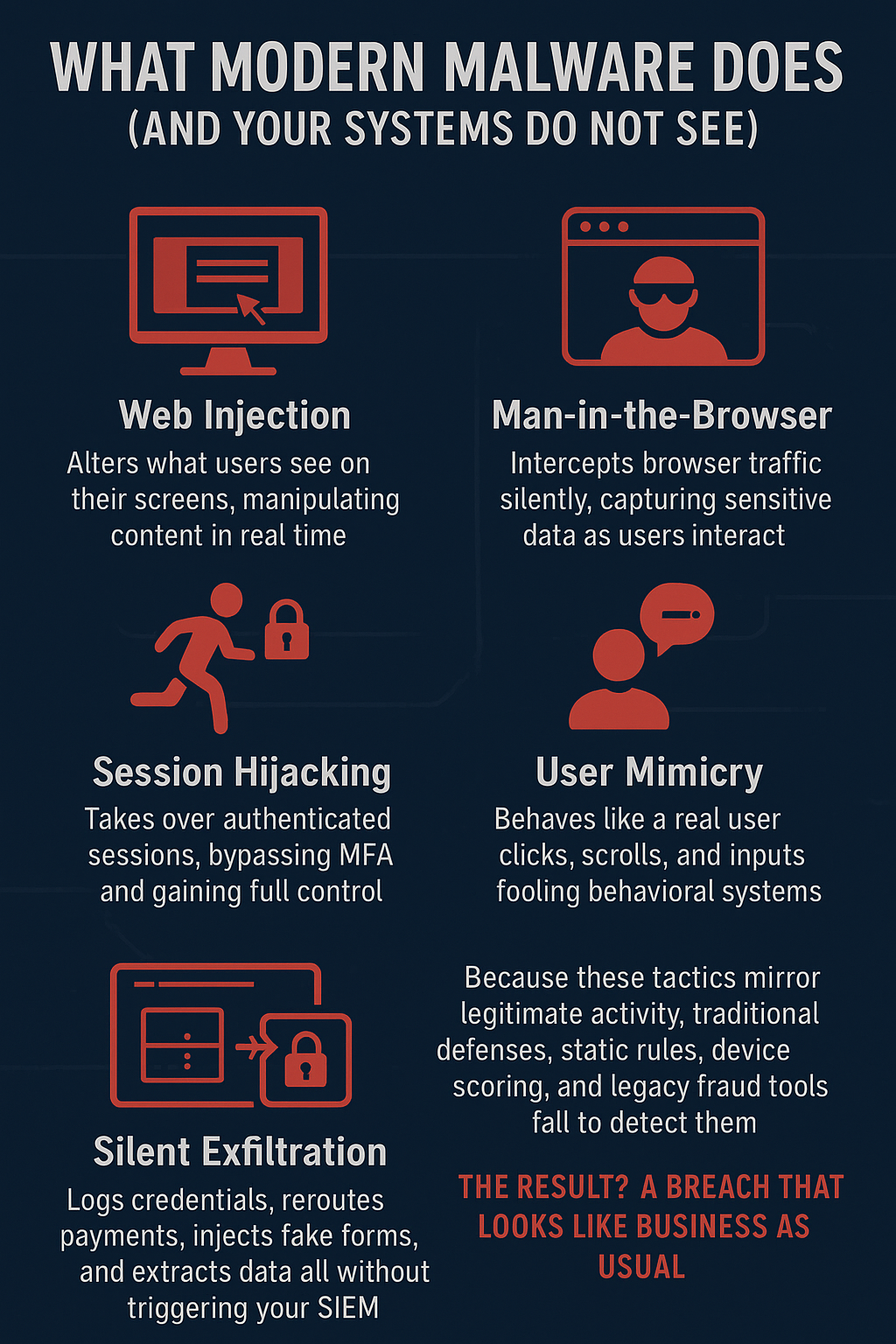
Modern malware isn’t just about infection it’s about orchestration. Today’s attacks are engineered to operate invisibly, blending into legitimate user behaviour while executing complex fraud operations beneath the surface.
Here’s how advanced malware operates undetected:
- Web Injection: Alters what users see on their screens, manipulating content in real time.
- Man-in-the-Browser: Intercepts browser traffic silently, capturing sensitive data as users interact.
- Session Hijacking: Takes over authenticated sessions, bypassing MFA and gaining full control.
- User Mimicry: Clicks, scrolls, and inputs like a real user — fooling behavioral systems.
- Silent Exfiltration: Logs credentials, reroutes payments, injects fake forms, and extracts data all without triggering your SIEM.
Because these tactics mirror legitimate activity, traditional defenses, static rules, device scoring, and legacy fraud tools fail to detect them. The result? A breach that looks like business as usual.
Inside the Malware Lifecycle: A Fraud-Focused Breakdown

Cybercriminals weaponize access through a series of calculated stages. Here’s how it unfolds:
Social Engineering
- Phishing emails
- SMS spoofing
- Fake mobile apps
Dropper & Delivery
- Malware kits
- Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms
Obfuscation
- Encrypted or packed payloads
- Designed to evade detection
Fileless Execution
- Runs in memory
- Uses PowerShell or scripts
- Leaves no trace on disk
Command & Control (C2)
- Establishes communication with attacker
- Receives instructions, sends stolen data
Session Manipulation
- Credential theft
- Fake fields and fund redirection
- Full account control
Crypto Wallet Exploitation
- Software vulnerabilities
- Fake login pages
- Unauthorized access without user consent
Prevention Tips: How Can You Stay Malware-Free?
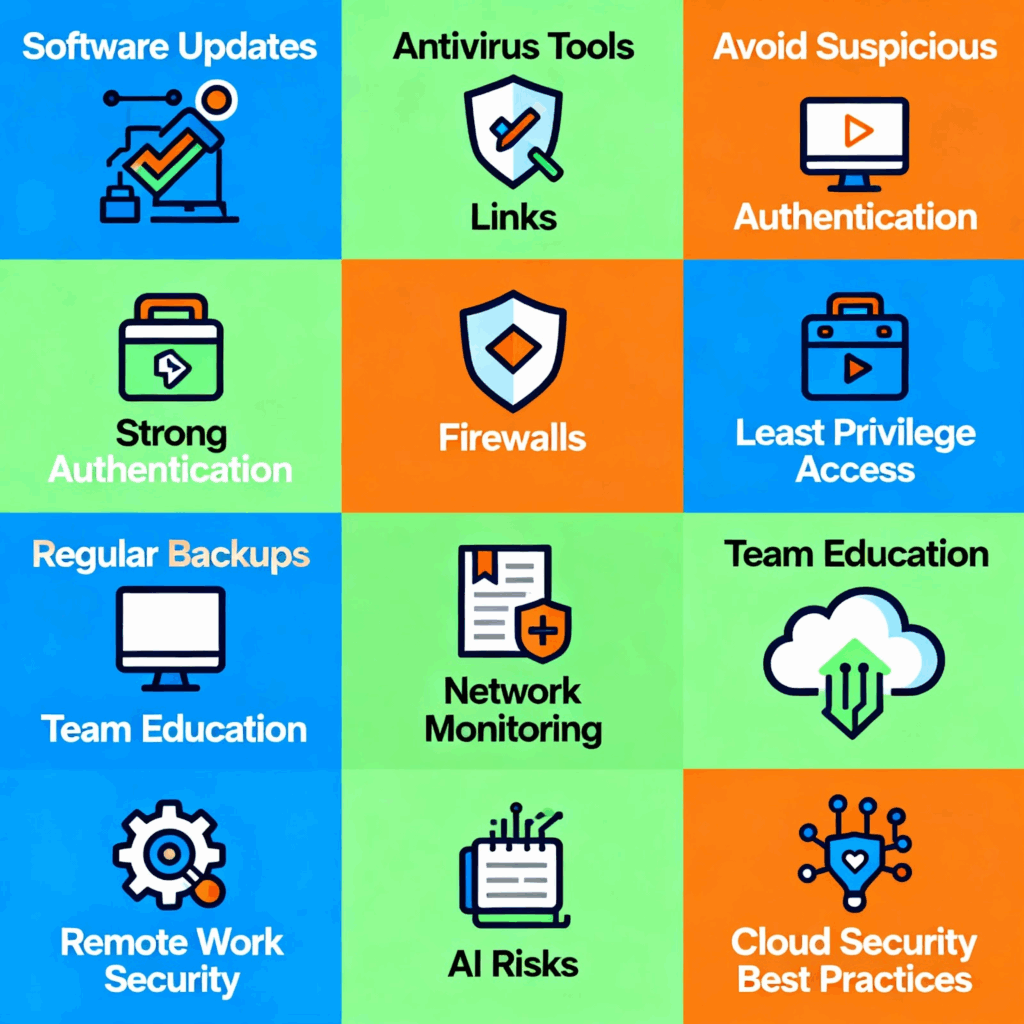
Whether you are a cybersecurity professional or a concerned user, these tips can help you stay protected:
Keep Software Updated
Outdated systems are prime targets. Enable automatic updates for operating systems, browsers, and apps.
Protect Your Devices with Point Wild UltraAV
Stay safe online with Point Wild UltraAV, the reliable antivirus and anti-malware tool built to keep your personal data secure. Whether it’s stopping viruses, blocking ransomware, protecting against infected USB drives, or defending against phishing attacks, UltraAV gives you real-time protection so you can browse, shop, and bank online with confidence. With automatic updates and an easy-to-use interface, Point Wild UltraAV is the smart choice for families and individuals who want hassle-free cybersecurity.
Avoid Suspicious Links and Attachments
Phishing emails often carry malware payloads. Hover over links before clicking and never download files from unknown sources.
Strengthen Authentication Practices
Add an extra layer of security beyond your password, making accounts significantly harder to access.
Enable Firewalls
Both hardware and software firewalls add a layer of defense against unauthorized access.
Practice Least Privilege
Limit user access to only what is necessary. Admin rights should be tightly controlled.
Backup Regularly
Maintain offline and cloud backups. In case of ransomware, backups can be your lifeline.
Educate Your Team
Conduct regular training on malware awareness, phishing detection, and safe browsing habits.
Monitor Network Traffic
Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools to spot anomalies.
Remote Working Security
With hybrid work now a mainstay option in many job roles, remote work security is more important than ever. A comprehensive approach includes tips on bolstering home Internet security by changing default router settings and updating firmware when available.
Artificial Intelligence
AI cybersecurity awareness topics to teach employees include the danger of feeding confidential or sensitive data into these tools, and the use of generative AI by threat actors to create convincing phishing emails or other scams.
Cloud Security
The average business now uses SaaS apps, and the cloud revolution extends to cloud infrastructure and data storage. Employees who use any cloud service need to know about specific cloud security practices, such as:
- Only using vetted and approved apps.
- Sharing data securely.
- Using configuration management tools to avoid misconfigurations.
- Encrypting data before uploading it to cloud services.
What does Point Wild-Lat61 Threat Intelligence do?
The Lat61 Threat Intelligence team unites seasoned threat researchers and cybersecurity specialists with deep experience in frontline defense. Leveraging Point Wild’s cutting-edge security technologies, Lat61 integrates seamlessly into a unified, API-enabled backend system. This enables the detection of sophisticated, multi-vector cyberattacks and delivers actionable insights to strengthen protection across the digital landscape.
Research by the Lat61 Threat Intelligence Team includes:
AI Malware: AI malware is self-evolving malicious software that uses artificial intelligence to dynamically adapt its attack methods and evade detection by learning from its environment, system defenses, and user behaviour. These intelligent threats can mimic legitimate behavior, find novel vulnerabilities, automatically update their code (polymorphism), and scale their attacks more rapidly.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/your-viral-3d-selfie-is-a-hackers-treasure
Stealer: Stealer malware, or “infostealers,” are a type of malicious software designed to secretly collect sensitive information from a victim’s computer or mobile device. They operate stealthily in the background, making them difficult to detect, and can harvest a wide range of personal, financial, and corporate data.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/raven-stealer
Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that restricts access to a victim’s computer or files, demanding a ransom payment, typically in cryptocurrency, to restore access. Attackers encrypt or lock files, threatening to steal, delete, or publish the data unless a ransom is paid.
Ref : https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/dragonforce-ransomware
Cryptojackers (Cryptomining malware): This malware hijacks a device’s processing power to mine cryptocurrency for the attacker without the user’s consent. It typically runs silently in the background, but can slow down the device, cause overheating, and increase electricity costs.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/coinminer
Trojan: Trojan malware is a type of malicious software disguised as a legitimate program, game, or file to trick users into installing it.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/sakula-rat
Backdoor: Backdoor malware creates secret entry points into systems, bypassing normal security and authentication to grant attackers remote access for stealing data, installing more malware, or manipulating the system.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/analysis-of-backdoor-win32-buterat.
Android Malware: Android malware targets mobile devices by disguising itself as legitimate apps to steal personal or financial data. Once installed, it can monitor activity, intercept messages, and even take control of the device. Users should download apps only from trusted sources and keep their devices updated to stay protected.
Ref: https://www.pointwild.com/threat-intelligence/crocodilus-global-android-malware
Final Thought:
Cybersecurity Awareness Month isn’t just a temporary initiative. It represents a long-term commitment to building a safer digital world. The message encourages everyone to take this opportunity to learn more about cyber threats, help others stay informed, and adopt secure habits online. The key idea is that awareness, knowing what to look out for and how to respond is one of the most powerful tools we have to prevent cybercrime.